Clinical Evidence of Syneo for CMPA
Compared with healthy breastfed infants, the gut microbiota of infants with CMA is often out of balance.6-10 This imbalance (dysbiosis) is typically characterised by:
Lower levels of beneficial Bifidobacteria7,8
Higher levels of adult-like bacteria such as Clostridia and Eubacteria6,7,9
A balanced gut microbiota is important for the development of the immune system.11-13
Breastmilk is the best source of nutrition for infants with CMA.14,15 It contains prebiotic oligosaccharides and beneficial bacteria that support the development of a balanced gut microbiota.16,17
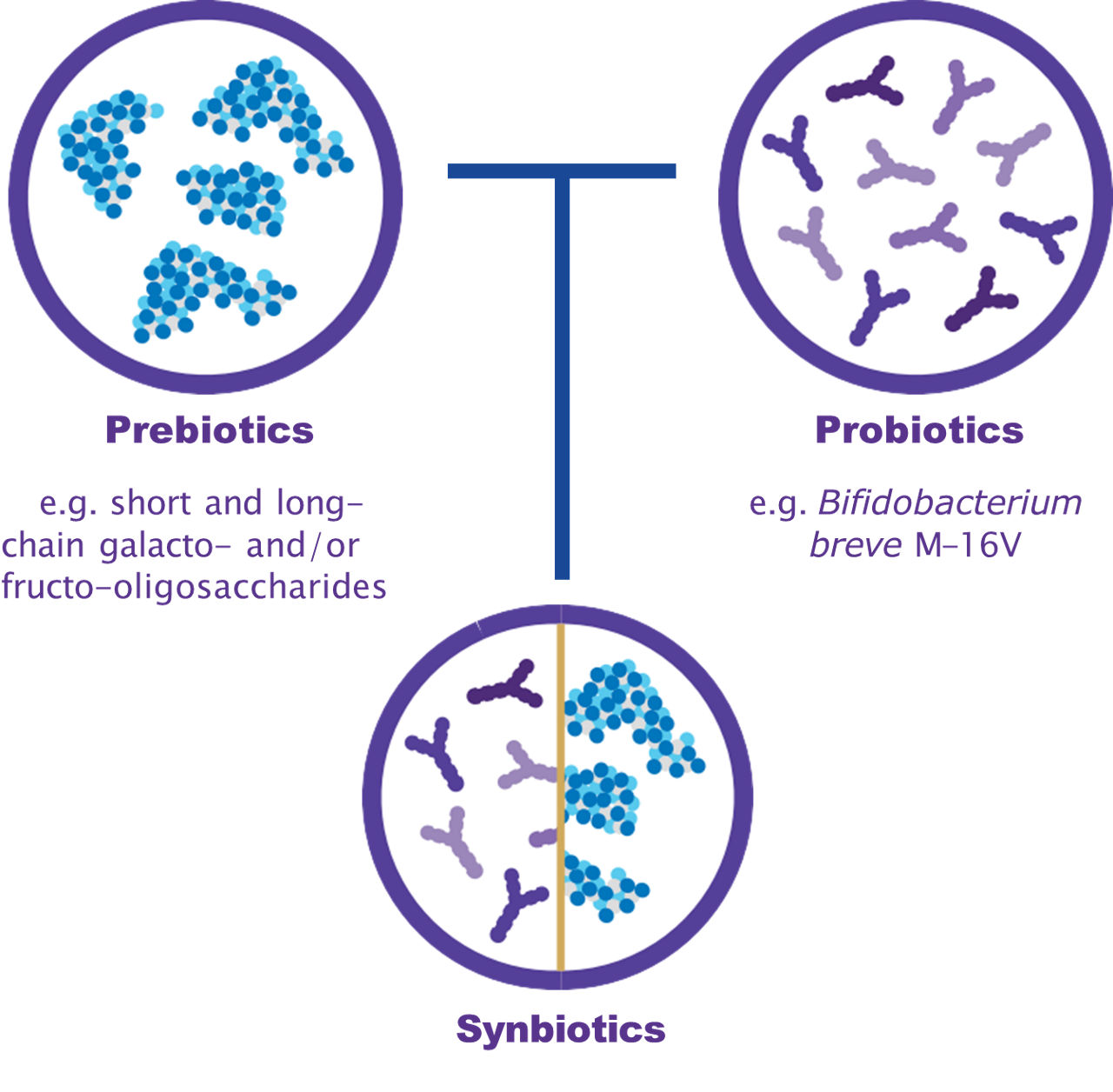
Synbiotics are a combination of prebiotics and beneficial bacteria (probiotics) that work synergistically together.18
For formula-fed infants with CMA, over 10 years of research with allergic infants has shown the benefits of supplementing hypoallergenic formula with synbiotics.*6,10,19-26
Well-tolerated10,19,20
Rebalances the gut microbiota6,10,21-24
Supports normal growth10,19-22
Improved clinical outcomes vs non- synbiotic formulas20,22,24-26
Randomised controlled trials
van der Aa 201024
12-week RCT of infants with AD (n=90)
Compared to an EHF without synbiotics, those in the synbiotic EHF group showed:
- A gut microbiota closer to that of a healthy breastfed infant
- Reduced constipation (p=0.01) and dry stools (p=0.001)
- Reduced AD severity* (p=0.04)
van der Aa 201125
Follow-up from 12-week RCT of infants with AD (n=75)
Compared to an EHF without synbiotics, those in the synbiotic EHF group showed:
- A significantly lower prevalence of asthma-like symptoms at one-year follow-up (p=0.04)
- Significantly less asthma medication use at one-year follow-up (p=0.02)
Systematic review
Sorensen 202122
Meta-analysis of four RCTs of infants with CMA (n=410)
Compared to an AAF without synbiotics, a synbiotic AAF supported:
- A gut microbiota closer to that of a healthy breastfed infant
- Fewer infants with infections (p=0.001)
- Lower overall medication use (p<0.001)
- Fewer hospital admissions due to infection (p=0.036)
- Potential healthcare cost savings
Cohort studies
Sorensen 202126
Retrospective matched cohort study of infants with CMA using data from the THIN GP database (n=148)
Compared to an AAF without synbiotics, a synbiotic AAF was associated with:
- Fewer GI, skin and/or respiratory symptoms* (p<0.001)
- A lower rate of dietitian contacts (p=0.014)
- Lower rates of infections (p<0.001) and medication prescriptions (p<0.001)
- A shorter clinical journey† (p<0.001)
- Potential healthcare cost savings
Hubbard 202220
Single-arm, prospective study of infants with non-IgE CMA (n=29)
Compared to EHFs without synbiotics*, a synbiotic EHF supported:
- Reduced incidence and severity of constipation, abdominal discomfort and wind (p<0.05)
- Reduced rhinitis severity and itchy eyes (p<0.05)
- Reduced AD severity† (p=0.03)
- A lower mean number of hospital visits and medication prescriptions in the 6 months after initiation‡ (p<0.05)
- Improved caregiver quality of life scores# (p=0.004)
Discover the only hypoallergenic formula range with synbiotics*†
*Synbiotic blend: Bifidobacterium breve M-16V (probiotic) & short and long-chain galacto- and/or fructo-oligosaccharides (prebiotic).
AAF: Amino Acid-based Formula; AD: atopic dermatitis; CMA: Cow’s Milk Allergy; EHF: Extensively Hydrolysed Formula; FAQL-PB: Food Allergy Quality of Life-Parental Burden; GI: gastrointestinal; HCP: healthcare professional; PO-SCORAD: Patient‐Orientated SCORing AD; RCT: Randomised Controlled Trial; THIN: The Health Improvement Network
van der Aa 201024: *Subgroup of n=48 infants with IgE associated AD.
Sorensen 202126: *Diarrhoea, constipation, flatulence, vomiting, reflux, bloody stools, mucus in stools, colic, eczema & urticaria. †Clinical journey endpoint measured as being asymptomatic and not requiring a hypoallergenic formula prescription for at least 3 months.
Hubbard 202220: *Baseline non-synbiotic formula (n=27 out of n=29 well-established on a non-synbiotic EHF). †Significant reduction in PO-SCORAD in subgroup of n=6 infants with more severe AD at baseline.
‡Follow-up arm of study n=13. #Assessed via FAQL-PB questionnaire.
1. Luyt, et al. Clin Experimental Allergy. 2014;44(5):642-72.
2. Meyer, et al. Pediatr Allergy Immunol. 2018;29(7):689-704.
3. Fox, et al. Clin Transl Allergy. 2019;9:40.
4. Koletzko, et al. JPGN. 2012;55(2):221-9.
5. Grimshaw, et al. Clin Transl Allergy. 2016;6:1.
6. Candy, et al. Pediatr Research. 2018;83(3):677-86.
7. Canani, et al. ISME J. 2016;10(3):742-50.
8. Harmsen, et al. JPGN. 2000;30(1):61-7.
9. Thompson- Chagoyan, et al. Pediatr Allergy Immunol. 2010;21:e394-400.
10. Burks, et al. Ped Allergy Immunol. 2015;26(4):316-22.
11. Martin, et al. Benef Microbes. 2010;1(4):367-82.
12. West, et al. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2015;135(1):3-13.
13. Wopereis, et al. Pediatr Allergy Immunol. 2014;25(5):428-38.
14. WHO. Infant and young child feeding, 2003.
15. Vandenplas, et al. J Asthma Allergy. 2021;14:1243-56.
16. Moossavi, et al. Front Pediatr. 2018;6:197.
17. Boehm, et al. J Nutr. 2007;137(3Suppl.2):847S-9S.
18. Pandey, et al. J Food Sci Technol. 2015;52(12):7577-87.
19. Harvey, et al. Pediatr Res. 2014;75(2):343-51.
20. Hubbard, et al. Immun Inflamm Dis. 2022;10(6):e636.
21. Abrahamse-Berkeveld, et al. J Nutr Sci. 2016;5:e42.
22. Sorensen, et al. Nutrients. 2021;13(3):935.
23. Fox, et al. Clin Transl Allergy. 2019;9:5.
24. van der Aa, et al. Clin Exp Allergy. 2010;40(5):795-804.
25. van der Aa, et al. Allergy. 2011;66(2):170-7.
26. Sorensen, et al. Nutrients. 2021;13(7):2205.
27. Kinnear, et al. 2021 HCP & parent survey – AAF + synbiotics, Poster presentation at the 8th International Conference on Nutrition & Growth conference, accepted May 2021.
28. Data on file. 2023 Neocate Syneo and Pepti Syneo experience survey. Parent survey, n=90 parents, HCP survey n=120 HCPs. Jan 2023.
29. Market comparison of UK EHF and AAF data cards, September 2023.
Accurate at publication: October 2023
Help us provide information most relevant to you
Please ensure your role and areas of interest are up to date.