Aptamil Pepti 1
Aptamil Pepti 1 is a whey-based extensively hydrolysed formula (EHF) for the dietary management of Cow’s Milk Allergy. Aptamil Pepti 1 is a nutritionally complete hypoallergenic formula, suitable as a sole source of nutrition from birth.

Superior palatability
Aptamil Pepti 1 is part of the UK’s most palatable EHF range.1,2 It contains whey protein and lactose for superior palatability compared with a casein-based hydrolysate.3
According to UK healthcare professionals surveyed, the benefits of superior palatability include:1
Increased chance of non-rejection
Reduced likelihood of repeat visits to a healthcare professional due to a decreased need to switch to another formula
Reduction in feed waste and healthcare costs
Galacto-oligosaccharides and Fructo-oligosaccharides (GOS/FOS)
Aptamil Pepti 1 includes the prebiotic blend GOS/FOS, which is clinically proven to:
- Bring the intestinal microflora closer to that of a breastfed baby4
- Reduce the number of potential pathogens in the gut5
- Reduce the incidence of atopic dermatitis6-8
- Reduce the occurrence of infections7
- Reduce the number of antibiotic courses required7
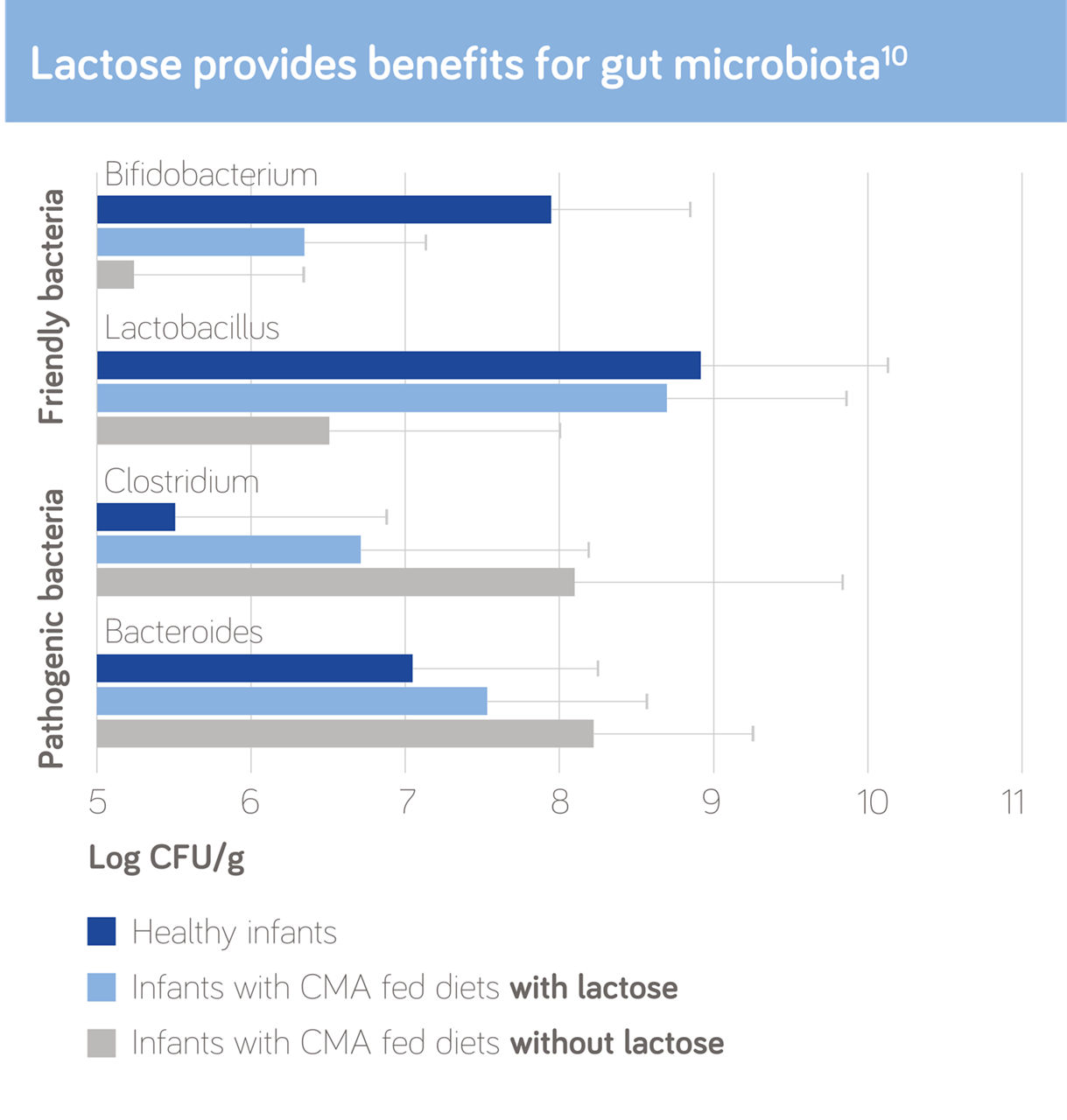
Lactose in the first 1000 days
Lactose plays an important role in the development of infants in the first 1000 days:
- Lactose is the primary carbohydrate in breastmilk9
- It provides benefits for an infant’s gut microbiota.10 Diets without lactose may have disadvantages for the composition of the infant’s gut microbiota11
- It helps to stimulate the absorption and retention of calcium, which is key for bone mineralisation9
- Lactose improves palatability12
FAQs
What is an extensively hydrolysed formula (EHF)?
The proteins in extensively hydrolysed formulas have been hydrolysed (broken down) into much smaller pieces.
Aptamil Pepti 1 has been designed for the dietary management of cow's milk allergy, so the milk proteins present have been broken down into smaller pieces (hydrolysed) to reduce the likelihood of them causing an allergic reaction.11
What is the difference between Aptamil Pepti 1 and Aptamil Pepti 2?
Aptamil Pepti 2 has higher levels of certain vitamins and minerals, like calcium and iron, to support the weaning diet of an infant with Cow’s Milk Allergy. It is suitable for the dietary management of Cow’s Milk Allergy from 6 months of age.
† Product can be provided to patients upon the request of a Healthcare Professional. They are intended for the purpose of professional evaluation only.
1. Maslin K et al. Palatability of hypoallergenic formulas for cow’s milk allergy and healthcare professional recommendation. Pediatr. Allergy Immunol. 2018; 29(8): 857-862. *A home usage test assessment was carried out between 16/11/16 and 9/12/16 on the 4 products indicated for cows’ milk allergy from birth and included 100 UK healthcare professionals.
2. Data on file, updated independent taste panel report, Campden BRI, October 2020. n=102 HCPs, Campden BRI blind home usage taste testing, n=102 Dietitians and General Practitioners, n=82 parents. Aptamil Pepti 1 & Pepti Syneo vs all UK EHFs suitable for infants from birth.
3. Venter C. Cow’s milk protein allergy and other food hypersensitivities in infants. J Family Healthcare. 2009;19 (4):130-131.
4. Moro G et al. Dosage-related bifidogenic effects of galacto- and fructooligosaccharides in formula-fed term infants. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 2002;34(3):291-5.
5. Knol J et al. An infant formula containing prebiotics changes the intestinal microflora of term infants. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 2003;3:566.
6. Arslanoglu S et al. Early neutral prebiotic oligosaccharide supplementation reduces the incidence of some allergic manifestations in the first 5 years of life. J Biol Regul Homeost Agents. 2012;26(3):49-59.
7. Arslanoglu S et al. Early dietary intervention with a mixture of prebiotic oligosaccharides reduces the incidence of allergic manifestations and infections during the first two years of life. J Nutr 2008;138:1091-5.
8. Moro G et al. A mixture of prebiotic oligosaccharides reduces the incidence of atopic dermatitis during the first six months of age. Arch Dis Child 2006;91:814-9.
9. Heyman MB. Lactose intolerance in infants, children and adolescents. Pediatrics 2006;118:1279-86.
10. Francavilla R et al. Effect of lactose on gut microbiota and metabolome of infants with cow's milk allergy. Pediatr Allergy Immunol 2012;23(5):420-7.
11. Høst A et al. Dietary products used in infants for treatment and prevention of food allergy. Arch Dis Child 1999;81(1):80-4.
12. Koletzko S et al. Diagnostic approach and management of cow's milk protein allergy in infants and children: ESPGHAN GI Committee practical guidelines. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 2012;55:221-9.
Accurate at time of publication: October 2023

